Game > GameAnvil > 서버 개발 가이드 > 게이트웨이 노드 구현
Gateway Node
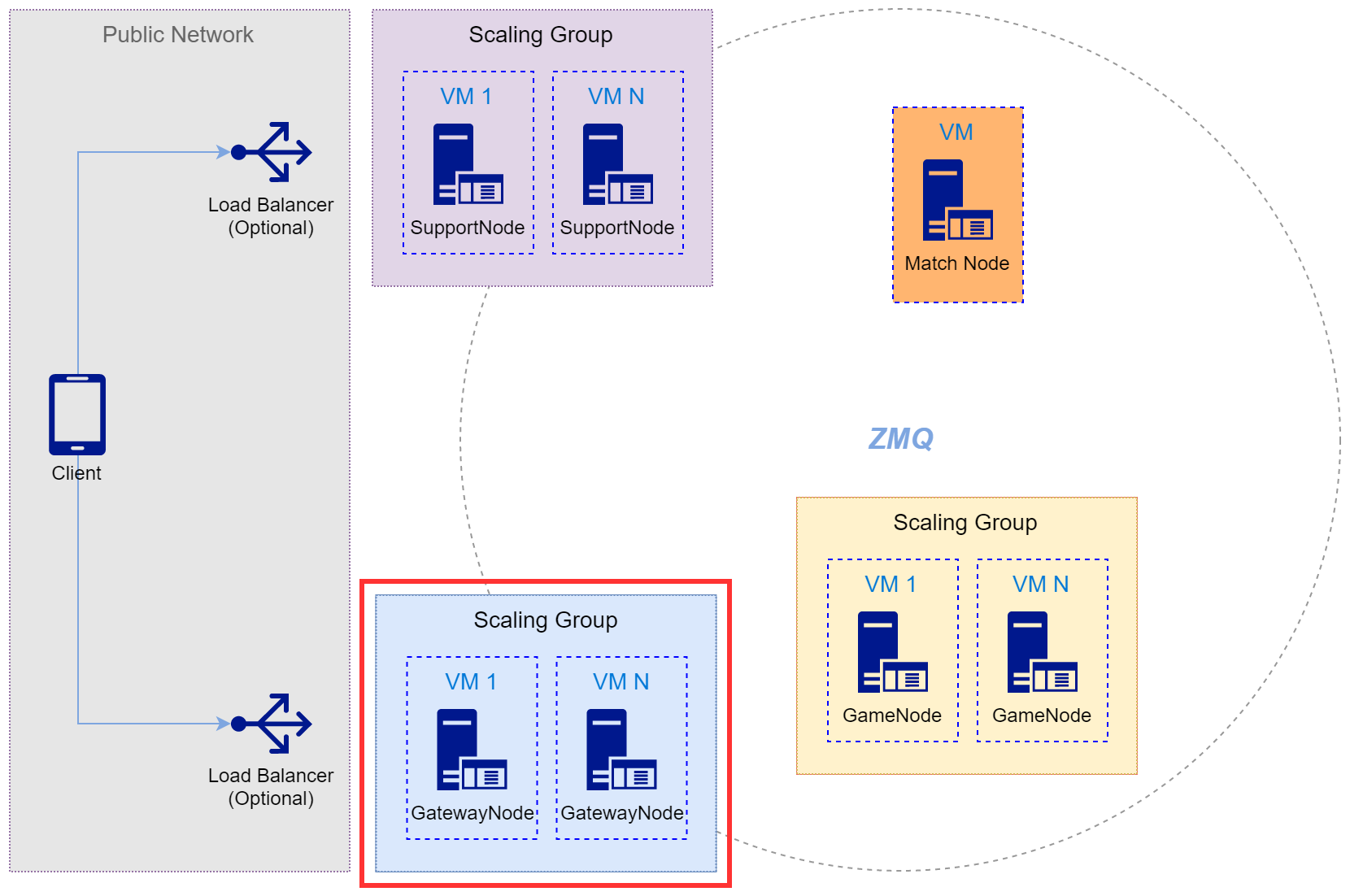
GatewayNode는 클라이언트가 접속하는 관문(Gateway)입니다. 즉, 클라이언트의 커넥션과 게임 서비스에 대한 세션을 관리합니다. 이때, 클라이언트는 게임을 진행하기 위해 반드시 GatewayNode에 접속한 후 인증을 완료해야 합니다. 이들의 관계는 다음 그림과 같습니다.
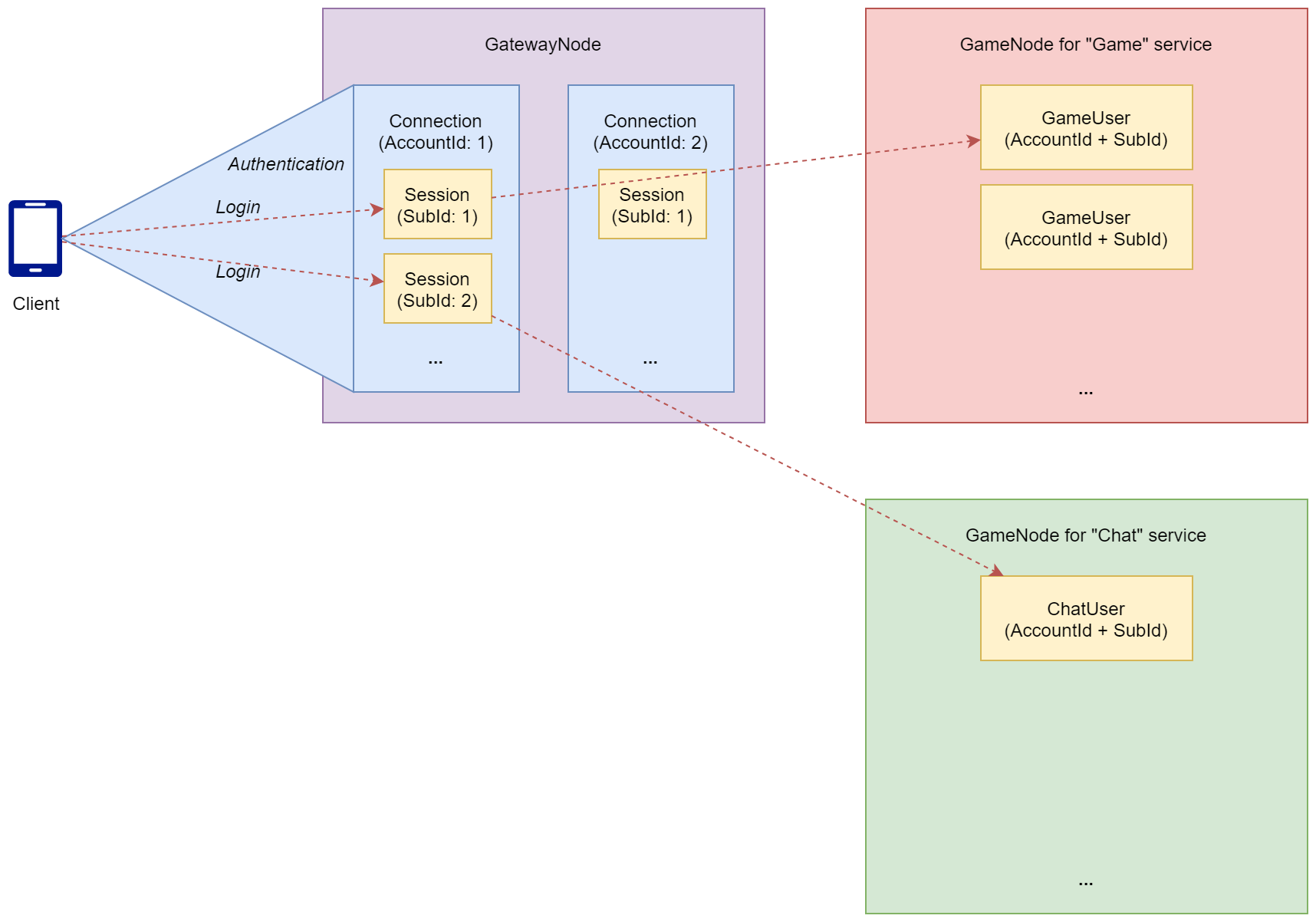
일반적으로 클라이언트는 GatewayNode로 하나의 커넥션을 맺습니다. 이때, 해당 커넥션에 대해 인증 절차를 진행하고, 성공한 경우에 한해 하나 이상의 세션을 생성할 수 있습니다. 각각의 세션은 클라이언트와 유저 사이의 논리적 연결 단위입니다. 위의 그림은 클라이언트가 하나의 커넥션을 통해 Game 서비스와 Chat 서비스로 세션을 생성한 모습입니다. 이러한 구조는 의도치 않게 클라이언트의 접속이 끊기더라도, 간단하게 세션 복구 (Session Recovery)를 가능하게 합니다.
GatewayNode 구현
이러한 GatewayNode는 BaseGatewayNode 클래스를 상속하여 공통 콜백 메서드만 재정의하면 됩니다. 이러한 공통 콜백 메서드는 그 이름이 용도를 명확하게 설명하고 있습니다. 또한 이렇게 구현한 클래스를 엔진에 등록하기 위해 @GatewayNode 애너테이션을 사용합니다.
@GatewayNode // 이 GatewayNode 클래스를 엔진에 등록
public class SampleGatewayNode extends BaseGatewayNode {
/**
* 초기화할 때 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onInit() throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* Ready 되기 전에 처리할 부분을 위해 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onPrepare() throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* Ready 될 때 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onReady() throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* pause 될 때 호출
*
* @param payload contents 에서 전달하고자 하는 추가 정보
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onPause(Payload payload) throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* resume 될 때 호출
*
* @param payload contents에서 전달하고자 하는 추가 정보
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onResume(Payload payload) throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* shutdown 명령을 받으면 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onShutdown() throws SuspendExecution {
}
}
Connection 구현
커넥션은 클라이언트의 물리적 접속 자체를 의미합니다. 클라이언트는 고유한 AccountId를 이용하여 커넥션 상에서 인증 절차를 진행할 수 있습니다. 인증이 성공할 경우 해당 AccountId는 생성된 커넥션에 매핑됩니다.
이러한 커넥션은 다음과 같이 BaseConnection을 상속한 후 콜백 메서드들을 재정의합니다. 이때, 임의의 플랫폼에서 인증한 후 획득하는 유저의 키 값 등을 AccountId로 사용할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어 Gamebase를 통해 인증한 후 UserId를 획득하면 이 값을 GameAnvil의 인증 과정에서 AccountId로 사용할 수 있습니다. 또한 GatewayNode 구현과 마찬가지로 구현한 클래스를 엔진에 등록하기 위해 @Connection 애너테이션을 사용하고 있습니다.
@Connection // 이 커넥션 클래스를 엔진에 등록
public class SampleConnection extends BaseConnection<SampleGameSession> {
/**
* authenticate 시에 호출
*
* @param accountId 계정 아이디
* @param password 계정 패스워드
* @param deviceId 클라이언트의 기기 아이디
* @param payload 클라이언트로부터 전달 받은 페이로드
* @param outPayload 클라이언트로 전달할 페이로드
* @return 인증 성공 여부: false이면 클라이언트와의 접속이 종료
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public boolean onAuthenticate(final String accountId, final String password, final String deviceId, final Payload payload, final Payload outPayload) throws SuspendExecution {
}
@Override
public void onPause() throws SuspendExecution {
}
@Override
public void onResume() throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* 클라이언트와 연결이 끊어졌을 때 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
public void onDisconnect() throws SuspendExecution {
}
}
이러한 콜백의 의미와 용도는 아래의 표를 참고하십시오.
| 콜백 이름 | 의미 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| onAuthenticate | 인증 | 클라이언트가 Authentication() API를 사용하여 커넥션에 대한 인증을 요청할 때 호출됩니다. 사용자는 여기에서 클라이언트가 보낸 인증 정보를 바탕으로 인증 처리를 진행할 수 있습니다. 만일 인증이 성공하면 true를 반환하고 실패하면 false를 반환해야 합니다. |
| onPause | 일시 정지 | 콘솔을 통해 GatewayNode를 일시 정지하면 해당 GatewayNode의 모든 커넥션에 대해 호출됩니다. 사용자는 노드가 일시 정지될 때 커넥션에서 추가로 처리하고 싶은 코드를 이곳에 구현할 수 있습니다. |
| onResume | 재개 | 콘솔을 통해 GatewayNode가 일시 정지 상태에서 다시 구동을 재개하면, 해당 GatewayNode의 모든 커넥션에 대해 호출됩니다. 사용자는 재개 상태에서 커넥션에 대해 처리하고 싶은 코드를 이곳에 구현할 수 있습니다. |
| onDisconnect | 접속 종료 | 클라이언트로부터 접속이 끊겼을 때 호출됩니다. 이때, 추가로 처리할 코드를 이곳에 구현합니다. |
| getMessageDispatcher | 처리할 패킷이 있음 | 노드에 처리할 메시지가 있을 때 반환시킵니다 사용자는 자신이 선언한 디스패처를 사용할 수 있습니다 자세한 내용은 메시지 처리를 참고하세요. |
Session 구현
커넥션을 성공적으로 맺은 클라이언트는 해당 커넥션상에서 서비스마다 하나씩 GameNode에 대한 논리적인 세션을 맺을 수 있습니다. GameAnvil은 내부적으로 커넥션의 AccountId와 세션의 SubId를 조합하여 전체 서버에서 고유한 세션을 구분할 수 있습니다.
이때, SubId는 사용자가 임의로 정한 규칙에 맞춰서 해당 커넥션 내의 아무 고유한 값으로 할당하면 됩니다. 즉, 서로 다른 커넥션은 동일한 SubId를 가질 수도 있습니다. 하지만 서로 다른 AccountId를 가지므로 구분이 가능합니다. 또한 구현한 세션 클래스를 엔진에 등록하기 위해 @Session 애너테이션을 사용하고 있습니다.
@Session // 이 세션 클래스를 엔진에 등록
public class SampleSession extends BaseSession {
private static MessageDispatcher<SampleSession> dispatcher = new MessageDispatcher<>();
static {
dispatcher.registerMsg(SampleGame.MsgToSessionReq.class, _MsgToSessionHandler.class);
}
@Override
public MessageDispatcher<SampleSession> getMessageDispatcher() {
return dispatcher;
}
/**
* login 호출 이전에 호출
*
* @param outPayload 클라이언트로 전달할 페이로드
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onPreLogin(Payload outPayload) throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* 로그인 성공 이후에 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onPostLogin() throws SuspendExecution {
}
/**
* 로그아웃 이후에 호출
*
* @throws SuspendExecution 이 메서드는 파이버를 suspend할 수 있음을 의미
*/
@Override
public void onPostLogout() throws SuspendExecution {
}
}
이러한 콜백의 의미와 용도는 아래의 표를 참고하십시오.
| 콜백 이름 | 의미 | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| onPreLogin | 로그인 전처리 | GameNode에 로그인을 요청하기 직전에 호출됩니다. 이때, 사용자는 매개변수로 전달된 출력용 페이로드(outPayload)에 임의의 값을 넣어서 로그인 요청에 실어 보낼 수 있습니다. 이 페이로드는 게임 노드에서 로그인 콜백을 처리할 때 그대로 전달됩니다. |
| onPostLogin | 로그인 후처리 | GameNode에 로그인을 완료한 후 호출됩니다. 로그인 완료 후에 세션에서 처리할 코드가 있다면 여기에 구현합니다. |
| onPostLogout | 로그아웃 후처리 | 로그아웃 처리가 완료된 후 호출됩니다. 로그아웃 이후에 세션에서 처리할 코드가 있다면 여기에 구현합니다. |
| getMessageDispatcher | 처리할 패킷이 있음 | 노드에 처리할 메시지가 있을 때 반환시킵니다 사용자는 자신이 선언한 디스패처를 사용할 수 있습니다 자세한 내용은 메시지 처리를 참고하십시오. |
Connection과 Session
클라이언트는 게이트웨이 노드로 접속합니다. 즉, 커넥션을 생성합니다. 이 커넥션을 통해 계정과 유저 정보를 바탕으로 인증과 로그인을 진행할 수 있습니다. 로그인까지 완료되면 임의의 게임 노드에 유저 객체가 생성됩니다. 이는 게이트웨이 노드와 해당 게임 노드 사이에 논리적인 세션이 생성되었음을 의미합니다. 이렇게 커넥션과 세션 생성이 완료되면 해당 유저는 게임 진행이 가능해집니다. 여기에 대해서는 바로 뒤에서 게임 노드를 설명할 때 다시 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
Session Recovery
만일, 클라이언트와 게이트웨이 노드 사이에 재접속이 발생하면 아래의 그림과 같이 세션 복구(Session Recovery)가 진행됩니다. 재접속을 하는 과정에서 클라이언트는 여러 대의 게이트웨이 노드 중 이전과 다른 곳에 커넥션을 시도할 수도 있습니다. 이 경우 유저 객체가 존재하는 게임 노드에 대한 위치 정보를 바탕으로 새롭게 세션을 복구합니다. 그러므로 유저는 게임 진행 중에 재접속을 하더라도 이전의 게임 상태를 이어갈 수 있습니다.
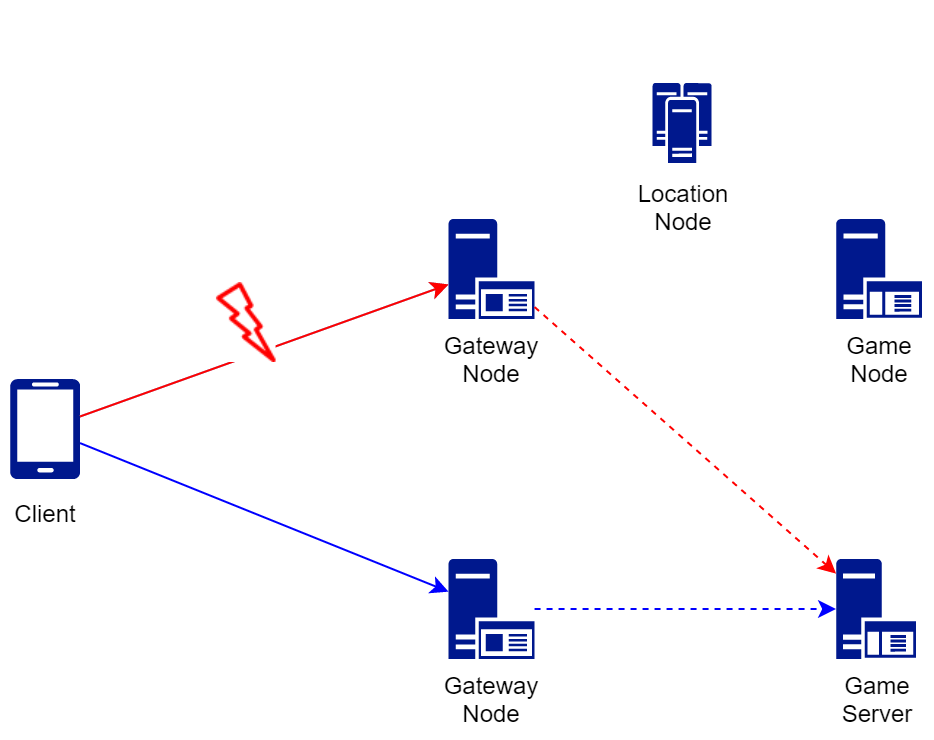
Location Node
앞서 살펴본 커넥션 복구 그림에서 로케이션 노드가 보입니다. 로케이션 노드는 GameAnvil이 내부적으로 유저와 방 등의 위치 정보를 관리하는 시스템 노드입니다. 사용자는 로케이션 노드에 대해 직접 구현하거나 사용할 수 없습니다. 하지만 위치 정보를 관리하는 로케이션 노드의 역할을 이해하는 것은 전체적인 GameAnvil 시스템의 흐름을 이해하는 데 도움이 되기 때문에 여기에서 간단하게 언급하고자 합니다.
위의 커넥션 복구를 예로 들어 보겠습니다. 클라이언트가 최초 접속을 하여 게임 노드로 로그인을 시도하는 과정에서 이와 관련된 세션과 유저에 대한 위치 정보는 모두 로케이션 노드에 저장됩니다. 그러므로 재접속을 진행할 경우에는 이전 접속 과정에서 저장해 두었던 이 위치 정보를 조회할 수 있습니다. 이러한 위치 정보는 GameAnvil 내부적으로 유저나 방의 위치 정보를 조회하고 이를 바탕으로 메시지를 전달하는 용도 등으로 매우 중요하게 사용됩니다.